Visual Abstract
Abstract
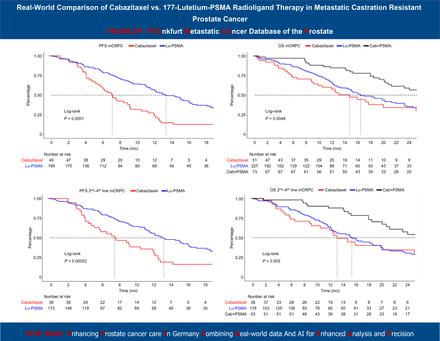
177Lu-vipivotide tetraxetan prostate-specific membrane antigen (177Lu-PSMA) therapy is under current scientific investigation and aims to become established in the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). However, real-world evidence in treatment comparison is scant. Methods: We relied on the FRAMCAP database and compared cabazitaxel versus 177Lu-PSMA therapy in mCRPC patients regarding progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Sensitivity analyses addressed second- to fourth-line mCRPC treatment to approximate current phase III patient selection criteria. Results: Of 373 patients, 14% received cabazitaxel, 65% received 177Lu-PSMA, and 21% received both. Patients undergoing 177Lu-PSMA therapy were significantly older than cabazitaxel patients (median, 72 y vs. 66 y; P < 0.01), and a higher proportion had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score of 2 or more (12% vs. 5.0%, P = 0.1). Rates of a prostate-specific antigen decline of at least 50% were 32% versus 0% for 177Lu-PSMA versus cabazitaxel. In outcome analyses, significant superior median PFS was observed for 177Lu-PSMA versus cabazitaxel (13.4 mo vs. 7.1 mo, P < 0.001), even after multivariable adjustment (hazard ratio, 0.38; P < 0.001). Regarding OS, rates also significantly differed, with median OS of 14.7 mo versus 16.5 mo versus 29.6 mo for cabazitaxel versus 177Lu-PSMA versus both treatments (P < 0.01). In sensitivity analyses of second- to fourth-line mCRPC treatment, PFS rates and median OS rates for cabazitaxel versus 177Lu-PSMA versus both therapies qualitatively remained the same as for the entire cohort. Conclusion: In a real-world setting, 177Lu-PSMA provides significantly better PFS and qualitatively better OS rates than does cabazitaxel chemotherapy and should therefore be considered a valuable treatment option for advanced mCRPC patients according to the European Medicines Agency approval.
Footnotes
Published online Nov. 14, 2024.
- © 2025 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
SNMMI members
Login to the site using your SNMMI member credentials
Individuals
Login as an individual user